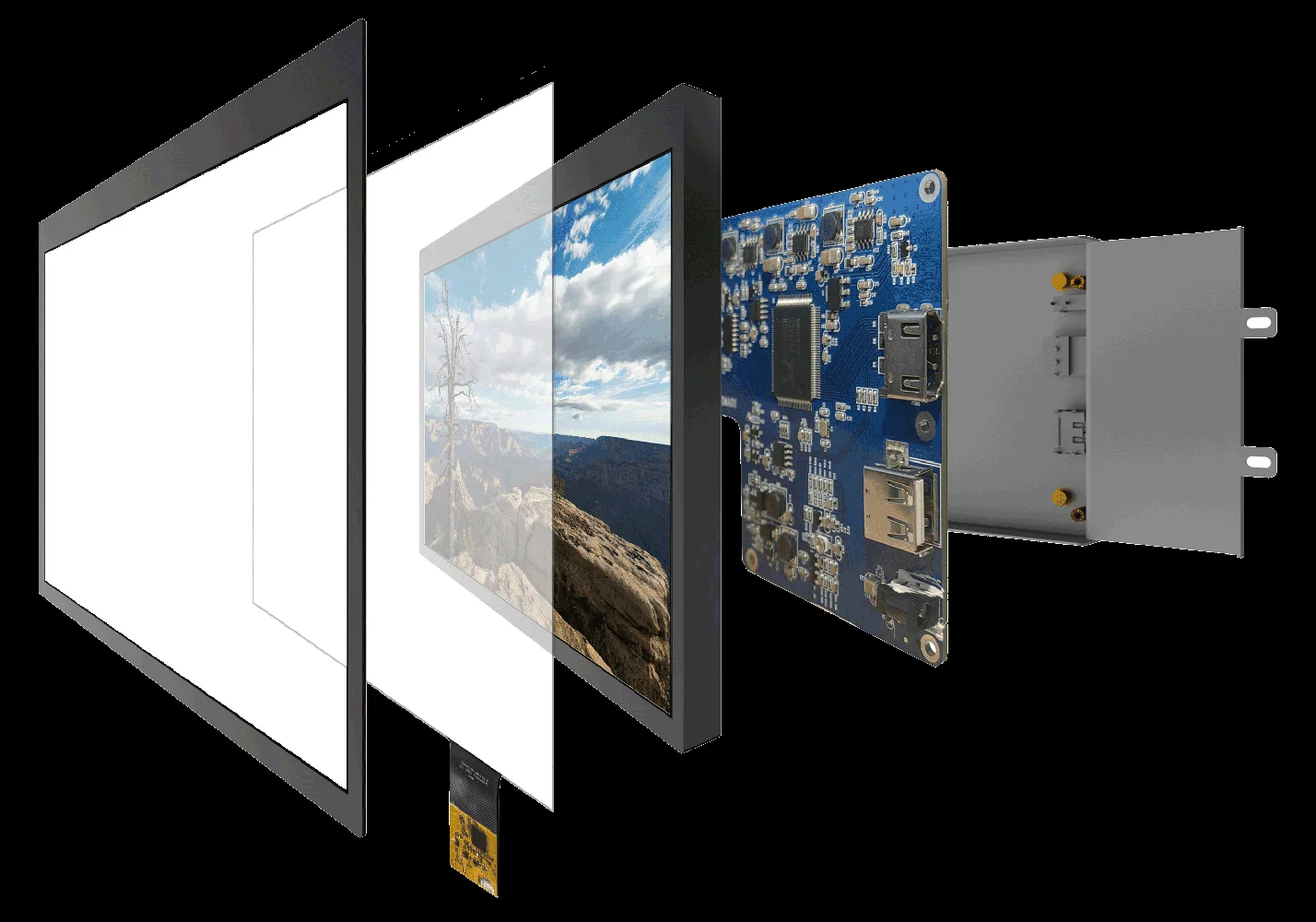
Touch screens are ubiquitous—found in smartphones, vehicles, retail checkouts, and industrial equipment. However, not all touch screens function alike. Two prevalent types are capacitive and resistive. They appear similar but operate differently and serve distinct purposes. This guide explains capacitive touch screen how it works, how resistive touch screen works, and the capacitive touch screen and resistive difference to help you determine which is better for your needs.
What Are Capacitive and Resistive Touch Screens?
Capacitive Touch Screen: How It Works
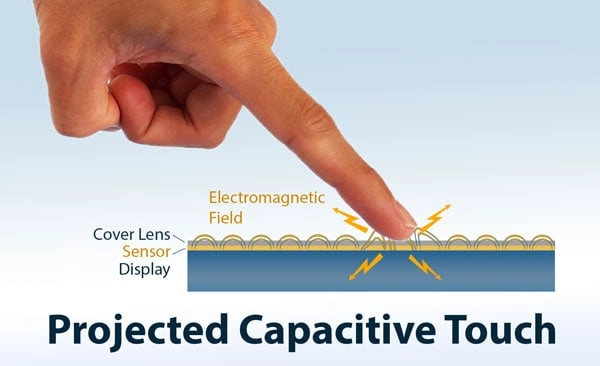
A capacitive touch screen detects touch using your body’s natural electrical charge. When your finger contacts the screen, it alters the local electrostatic field. The screen consists of a glass layer coated with a transparent conductor, indium tin oxide (ITO). This layer lies beneath a protective glass panel. Upon contact, some of your body’s charge transfers to the screen. Sensors then pinpoint the exact location of the touch.
This method ensures swift and fluid responses. One of the key advantages of capacitive touch screen technology is its support for multi-touch gestures, such as pinch-to-zoom or two-finger scrolling. This explains why capacitive screens dominate smartphones and tablets. If you’ve wondered how does a capacitive touch screen work, it’s simple: your body completes an electrical circuit.
Resistive Touch Screen: How It Works
A resistive touch screen operates differently. It comprises two thin layers—one conductive, one resistive—separated by a tiny gap. When you press the screen with a finger, stylus, or any object, the layers connect. The screen then detects the pressure point.
Since it relies on pressure, a resistive screen responds to nearly any tool. This is valuable in settings where gloves or instruments are used, such as factories or medical facilities. However, resistive screens typically support only single-touch inputs, unlike capacitive screens. When exploring what is the difference between capacitive and resistive touch screen, the core distinctions are input detection and supported interactions.
Key Differences Between Capacitive and Resistive Touch Screens
Touch Sensitivity and Accuracy
Capacitive screens are highly responsive. They react to light touches instantly. However, they may struggle with precision for tiny buttons. Conversely, resistive screens require a firm press. This enhances accuracy for tasks like form-filling with a stylus.
When deciding which is better, consider your use case. For quick, casual interactions, capacitive excels. For precise, deliberate actions, resistive is often preferable.
Durability and Maintenance
Capacitive screens typically use glass, making them robust and easy to clean. They resist scratches and maintain a pristine appearance longer. Resistive screens feature a soft plastic top layer. This layer is prone to scratches and may need a protective cover. Over time, internal layers may lose precision. This prompts questions like how to repair a heat damaged resistive touch screen. Replacing the top layer or recalibrating the device often resolves the issue.
Visibility in Different Environments
Capacitive screens offer better visibility in bright light. Their fewer layers allow more light to pass through. Resistive screens, with more layers, reflect light, reducing clarity in sunlight. If you’re designing for outdoor use, capacitive or resistive touch screen visibility matters. Capacitive screens perform better here.
Cost and Application Suitability
Resistive screens are less costly to produce. This makes them common in budget-conscious devices like ATMs, ticket kiosks, and certain medical tools. They are straightforward and dependable. Capacitive screens are pricier but deliver a modern aesthetic and superior performance. Thus, they are preferred for consumer electronics.
Advantages of Capacitive Touch Screens
Superior User Experience
Capacitive screens provide a seamless, rapid response. They react in under 3 milliseconds and support multi-touch gestures. These include swiping with two fingers or pinching to zoom. This is why what is capacitive multi touch screen is often highlighted in phones and tablets.
Enhanced Durability
Glass surfaces enhance longevity. Capacitive screens resist scratches and endure wear better. They also withstand chemicals, making them suitable for medical environments.
Better Clarity and Brightness
With fewer layers, capacitive screens allow more light transmission. This results in a vivid, clear display. Images and videos appear sharper, with vibrant colors.
Where Are Resistive Touch Screens Still Used?
Industrial and Medical Equipment
Resistive screens excel where gloves or tools are necessary. They don’t require skin contact, making them ideal for labs, cleanrooms, and manufacturing plants. This answers where is resistive touch screen used in modern applications.
Budget-Conscious Applications
Resistive screens appear in cost-sensitive settings needing basic touch input. Examples include ATMs, restaurant ordering systems, and affordable handheld devices. This explains what devices use resistive touch screen today.
Repairing a Heat-Damaged Resistive Touch Screen
Heat exposure may cause resistive screen layers to misalign or separate. Often, replacing the top layer or recalibrating fixes the issue. This addresses queries about how to repair a heat damaged resistive touch screen, as repairs can extend device life.
Choosing the Right Touch Screen: Capacitive or Resistive?
Factors to Consider
Evaluate the device’s environment. Will it be used indoors or outdoors? Are gloves involved? What’s the budget? These factors clarify which is better: capacitive or resistive touch screen.
For sleek, gesture-driven interfaces, choose capacitive. For rugged, simple applications, resistive is ideal.
Capacitive Multi-Touch Screens: When to Use Them
Capacitive multi touch screens suit dynamic, interactive applications. They power gaming devices, info kiosks, and retail digital displays. If your project requires gestures or smooth scrolling, incorporate what is capacitive multi touch screen functionality.
Leading Capacitive Touch Screen Manufacturers and Solutions
Global Manufacturers Overview
Top capacitive touch screen manufacturers include 3M, Synaptics, and Cypress. They are renowned for innovation and quality. However, smaller firms offer customized solutions with personalized service.
Kadi Display’s Customization Services
Kadi Display specializes in high-quality, tailored touch displays. With over 20 years of experience, they provide LCM, TP, and PCBA solutions. Whether for industrial equipment or sleek tablets, Kadi Display delivers.
Their capacitive touch screens blend sensitivity and durability, fitting diverse environments. For those asking how to make a capacitive touch screen tailored to a product, Kadi Display provides bespoke support unmatched by larger brands.
FAQs About Capacitive and Resistive Touch Screens
How does a capacitive touch screen work?
It detects touch via your body’s electric charge through a conductive glass layer.
What devices use resistive touch screens?
They appear in ATMs, medical equipment, and older handheld devices.
Which is better: capacitive or resistive touch screen?
It depends—capacitive for intuitive, stylish interfaces; resistive for precise, rugged settings.
Can you repair a cracked capacitive touch screen?
Yes, often by replacing the top glass. Contact capacitive touch screen manufacturers like Kadi Display for assistance.
What is a capacitive multi-touch screen?
It detects multiple simultaneous touches, ideal for gestures like zooming or rotating.
Need a Custom Touch Screen Solution?
Partner with Kadi Display
Unsure about capacitive or resistive technology? Kadi Display’s experts can assist. With over 5,000㎡ of production space and fast prototyping, they craft displays suited to your needs—be it a sunlight-readable capacitive screen or a budget-friendly resistive panel.
Elevate your product with precision-engineered touch displays. Email Sales@sz-kadi.com or call +86-13662585086 for a free consultation!
Latest Blog & News
- Capacitive vs. Resistive Touch Screens: A Complete Guide to Differences, Advantages, and Applications
- How Does a Reflective LCD Display Work? A Comprehensive Guide
- What Causes Lines in LCD Display Modules? (And How to Fix Them)
- What is the difference between Edge-Lit and Full-Array Local Dimming?
- Why Is AOI So Important for FOG Bonding?