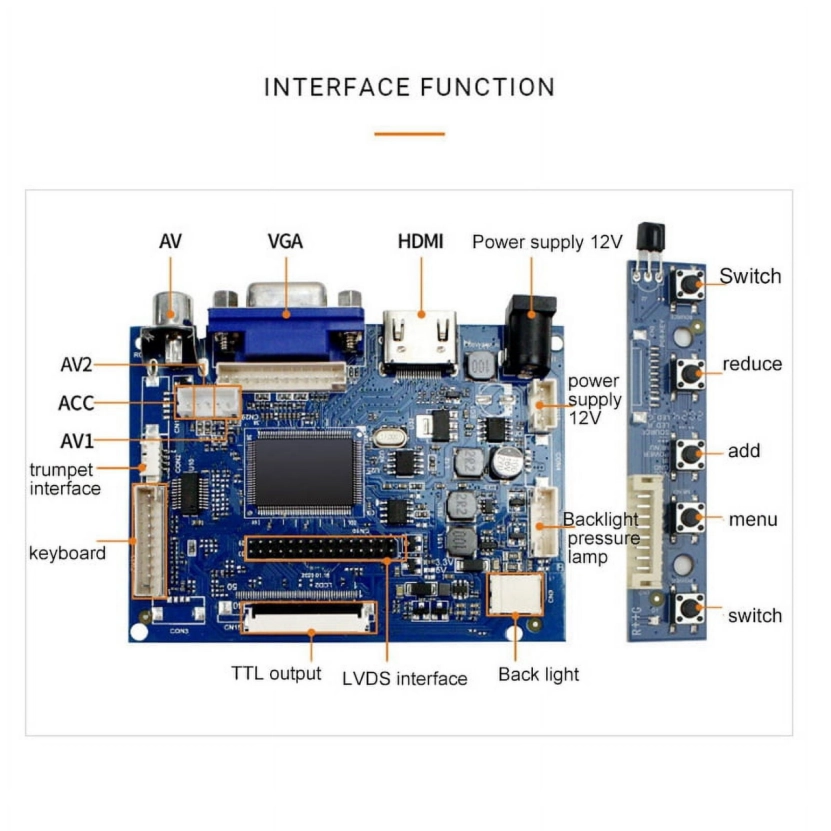
Display driver boards play a crucial role in modern electronic displays, controlling the transmission of signals and power to LCD, OLED, and LED screens. However, unstable output can lead to flickering, distortion, or even complete display failure. Understanding the root causes of instability can help engineers and technicians diagnose and resolve these issues effectively.
Common Causes of Unstable Output in Display Driver Boards
1. Power Supply Issues
A steady, well-controlled power source is crucial for Display driver boards to work smoothly. Any wobble or unevenness in power can directly affect how the screen performs.
1.1 Unstable Power Supply Voltage
Wavy power supply voltage can lead to uneven results in Display driver boards. If voltage dips too low, the board might not supply enough juice to run the screen. This causes flickering, fading, or full outages. On the flip side, too much voltage can overheat or harm delicate parts.
1.2 Excessive Power Supply Ripple
Power supply ripple means tiny voltage shifts, even in controlled setups. When this ripple grows too big, it adds static to the screen signal. This shows up as visible glitches like horizontal streaks, blinking, or shadowy images on the display.
1.3 Poor Grounding and Power Integrity
A flimsy or wrong ground link can bring electrical buzz and wobbles into Display driver boards. Ground loops happen when multiple ground ties create unexpected voltage gaps. These can spark flickering or odd screen actions. Solid grounding plans and power steadiness care are key to cutting these woes.
2. Signal Interference and Noise Issues
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) and signal static can greatly sway how Display driver boards perform. This leads to twisted pictures, shaky hues, or random blinks.
2.1 External Electromagnetic Interference
Display driver boards can pick up electromagnetic interference from nearby gadgets. Think high-voltage lines, radio senders, or wireless gear. This meddling can twist the video feed and make the screen unsteady.
2.2 Internal Crosstalk and Signal Reflection
Signal paths too close on the circuit board can cause crosstalk. Here, signals mess with each other. Also, poor matching between Display driver boards and the screen panel can cause signal bounce-back. This results in fuzzy visuals or ghost-like effects.
2.3 Poor Shielding and PCB Layout
Weak electromagnetic shielding leaves Display driver boards open to outside static. A smartly planned circuit board layout helps. Using grounded copper fills and fine-tuned path routing cuts interference down.
3. Component Failures and Aging
Over time, electronic pieces wear out. This affects how steady Display driver boards stay.
3.1 Capacitor Failure
Capacitors are key for voltage control and signal cleanup. When they wear from age, too much heat, or voltage strain, they falter. They can’t smooth voltage swings anymore. This leads to shaky screen output.
3.2 Resistor Value Drift
Resistors keep current and voltage in check within the driver setup. Over time, heat and electrical wear can shift their values. This messes with signal handling. It causes brightness or color oddities.
3.3 IC (Integrated Circuit) Malfunctions
The main chips on Display driver boards handle video signals and screen control. This includes the lead driver IC and backup processors. If these fail, big problems pop up. Think screen freezes, flickers, or total signal drops.
4. Thermal Management Problems
Display driver boards make heat while running. Too-high temperatures can hurt performance and shorten part life.
4.1 Overheat Protection Activation
Many boards have heat safety features. These cut power when temps climb too high. If Display driver boards get too hot, they might dim, flicker, or pause briefly. This prevents lasting harm.
4.2 Temperature Sensitivity of Components
Some parts, like capacitors and transistors, react to heat changes. Wild temperature swings can make them act oddly. This leads to unsteady output signals. Good cooling, like heat sinks and air flow, can ease these troubles.
5. PCB Design and Layout Issues
The circuit board design is critical for steady work. Bad choices here can add to unsteadiness in Display driver boards.
5.1 Inefficient Trace Routing and Layout
If signal paths stretch too far or cross power lines, the screen signal weakens. Without proper resistance control, it worsens. This can cause signal twists or timing slips.
5.2 Grounding and Shielding Problems
A solid grounding setup is vital for signal clarity. Weak grounding or poor shielding lets electrical static meddle with signal flow. This sparks unpredictable screen antics.
FAQs About Display Driver Board Stability
Q1: Why does my display flicker when connected to a driver board?
Flickering might stem from power source wobbles, shaky grounding, or electromagnetic meddling. Check the power feed. Ensure firm grounding. Use shielded cables to trim flickers.
Q2: How can I prevent overheating issues in my display driver board?
Keep air flowing well. Add heat sinks if needed. Don’t trap the board in tight spots where heat builds up.
Q3: What role do capacitors play in display driver board stability?
Capacitors steady power and zap unwanted static. Worn or old ones can spark voltage wobbles. This hits screen output hard.
Q4: How do I minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) affecting my display?
Use shielded cables. Keep high-power gadgets away from the screen. Ensure solid grounding and circuit board shielding design.
Q5: Can a faulty display panel cause instability even if the driver board is working fine?
Yes, a broken or mismatched screen panel can spark troubles. Think flickers, warped visuals, or signal drops. Always pair with a matching panel using right voltage and signal needs.
Q6: What are the signs of a failing display driver IC?
A dying driver IC might twist colors, spark random blinks, or cut signals fully. If swapping other parts doesn’t help, check or replace the driver IC.
Conclusion
For businesses and developers seeking high-quality, stable display solutions, Kadi Display is your trusted partner. With 20 years of industry expertise, Kadi Display provides custom LCM, touch panel, and PCBA services to accelerate your product development. Their extensive TFT-LCD, AMOLED, and embedded display solutions ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Looking for a customized display driver board that meets your exact needs? Contact Kadi Display today at Sales@sz-kadi.com or visit their website to explore cutting-edge display technologies that bring your vision to life!